INTRODUCTION
A suspension formulation is a type of disperse system where the insoluble solid particles are dispersed homogenously in the liquid phase. A good suspension must be in a homogenous form after shaking, easily poured from the container, has a uniform solid particle size and possess better feel and taste. Sediment that is formed upon storage has to be easily redispersed after shaking, forming homogenous suspension.
In general, suspension comprises of an active ingredient (solid phase) in a liquid carrier, a wetting agent, flavouring and colouring agents and preservatives. The function of a wetting agent such as tragacanth is to reduce the interfacial tension between the solid particles and the liquid. Suspension can be classified into a coarse suspension where the diameter of the particles is more than 1 µm or a colloidal suspension where the particle size is less than 1 µm. In pharmaceutical practice, suspension is used to improve the stability of the active ingredient, taste, and bioavailability.
OBJECTIVES
To study the effect of the composition of tragacanth on the physical appearance, the rate of sedimentation and viscosity of the suspensions of different compositions.
APPARATUS & MATERIALS
- Weighing balance
- Viscometer
- Centrifuge
- 100ml Beaker
- Weighing boat
- Pestle and mortar
- 50ml and 200ml Measuring cylinder
- Glass rod
- 150ml Plastic bottle
- 1ml Pipette and bulb
- 15ml Centrifudge tube
- Ruler
- Chalk
- Tragacanth
- Concentrated peppermint water
- Syrup BP
- Double-strength chloroform water
- Distilled water
PROCEDURE
- A suspension of Paediatric Chalk Mixture (150ml) is prepared using the formulation below:
| Chalk 3g
Tragacanth Refer to table 1 Concentrated Peppermint Water 0.6mL Syrup BP 15mL Double Strength Chloroform Water 75mL Distilled Water, q.s. 150mL |
Table 1
| Paediatric Chalk Mixture | Group | Tragacanth (g) |
| I | 1, 5, 9 | 0.0 |
| II | 2, 6, 10 | 0.1 |
| III | 3, 7, 11 | 0.3 |
| IV | 4, 8, 12 | 0.5 |
- 5 ml of the suspension that had been prepared was transferred into a weighing boat and labelled. The texture,clarity and colour was compared and explained.
- Then, 50 ml of the suspension that had been prepared was transferred into 50 ml measuring cylinder and the height of sedimented solid in the cylinder was measured every 0,5,10,15,20,25,30,35,40,45,50,55, and 60 minutes.

- 95 ml of the remaining suspension was poured inton100ml beaker and the viscosity of the suspension was determined by using Viscometer.

- 10 ml of the suspension was poured into centrifuge tube and the height of solid phase after centrifuged was measured (1000 rpm, 5 minute, 25 0C).
QUESTION
- Compare the physical characteristics of the suspensions and give your comment.
| Group | Amount of Tragacanth (g) | Texture | Clarity, appearance | Colour of suspension |
| 1 | 0.0 | Less viscous, rough texture and disperse easily | Less cloudy, has 2 layer | Less milky |
| 2 | 0.1 | Viscous | Moderately cloudy | Milky |
| 3 | 0.3 | Viscous | Opaque, cloudy | Milky |
| 4 | 0.5 | More viscous | Opaque, cloudy | Milky |
Tracaganth acts as a suspending agent to ensure the ingredients are even and proportional in the mixture to support the suspensoid. As the amount of tragacanth added to the formulation is increased, the suspension becomes more viscous. The more viscous a suspension is, the longer time it requires for the suspended particles to sediment and this allow the product to be poured out easily from the vehicle without particles clinging at the bottom. As the amount of tragacanth that added to the formulation increases, the more opaque and cloudy the product will be. The opacity and the cloudiness indicates that the disperse particles is totally dispersed in the medium. If no tragacanth is added to the formulation, the product will appear to be separated in two phase in which the supposed to be disperse phase seems to sediment at the bottom of the container. . But if sedimentation occurs, it will be easily redisperse and stay disperse in the medium for a longer time compared to those formulation without tragacanth.
- Plot graph of sediment against time. Give comments
| Time (minutes) | 0 | 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | 35 | 40 | 45 | 50 | 55 | 60 |
| Sediment height (mm) | 0 | 1 | 4 | 8 | 10 | 15 | 18 | 21 | 22 | 22 | 22 | 22 | 22 |
The graph above shows the relationship between the heights of sedimentation (mm) against time (min). Based on the graph, as the time taken increases, the height of sedimentation increases as well. The suspension was white in colour. Some light are used to observe the sedimentation clearly to avoid from making error. For the last 20 minutes, the height of sedimentation of suspension has become no change which is it maintain at 22 mm. This is because all of the Tragacanth in the suspension has been sedimentated.
- Plot average sediment height against time for suspensions with different Tragacanth content. Give comments
| Time(min) | Average Sediment Height (mm) | |||||||||||||
| 0 | 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | 35 | 40 | 45 | 50 | 55 | 60 | ||
| Tragacanth Content (g) | 0.0 | 95 | 18 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 |
| 0.1 | 12 | 11.8 | 11.6 | 11.5 | 11.5 | 11.5 | 11.4 | 11.3 | 11.3 | 11.3 | 11.2 | 11.1 | 10.9 | |
| 0.3 | 0 | 9 | 11 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 13 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 14 | |
| 0.5 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 8 | 10 | 15 | 18 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 22 | 22 | 22 | |
From the result, a comparison can be made based on the time needed for the first sediment to settle. The higher the amount of tragacanth mixed, the longer the chalk can suspend, thus needs longer time to sediment. For 0.0g and 0.1 tragacanth, the absence of sufficient suspending agents causes the suspension to be very unstable, thus enables sedimentation to occur rapidly as soon as the mixing stopped. At highest tragacanth 0.5g concentration, no sedimentation can be seen on the first few minutes, because the suspending agents allows the chalk particles to suspend longer.
Next, we can see an obvious difference in the sedimentation pattern in low and high concentration of tragacanth. At 0.0g, the sediment height become shorter as time passes before comes to a plateau and this pattern is inversely true for higher concentration (0.5g). This is due to the presence of tragacanth which makes the sediment is less packed, as compared to suspension with lower tragacanth concentration.
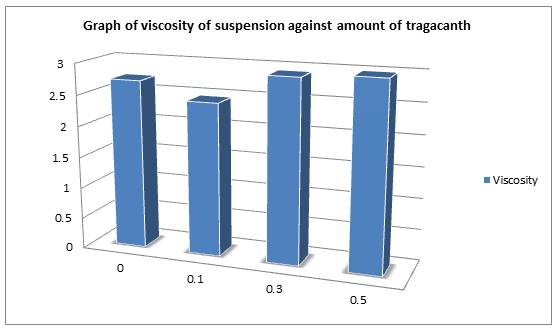
- Elaborate the viscometer analysis mechanism. Plot a graph on viscosity of suspension against Tragacanth content (g). Give comments
Viscometer is an instrument for the determination of viscosity. The most common types of viscometer are capillary, rotary, falling-sphere and ultrasonic.
In this experiment we use rotary viscometer. Rotational viscometers use the idea that the torque required to turn an object in a fluid is a function of the viscosity of that fluid. They measure the torque required to rotate a disk or bob in a fluid at a known speed.
‘Cup and bob’ viscometers work by defining the exact volume of a sample which is to be sheared within a test cell. The torque required to achieve a certain rotational speed is measured and plotted. There are two classical geometries in “cup and bob” viscometers, known as either the “Couette” or “Searle” systems. It is distinguished by whether the cup or bob rotates. The rotating cup is preferred in some cases because it reduces the onset of Taylor vortices, but is more difficult to measure accurately in instrument.
‘Cone and Plate’ viscometers use a cone of very shallow angle in bare contact with a flat plate. With this system the shear rate beneath the plate is constant to a modest degree of precision and deconvolution of a flow curve.
The advantages of this rotational viscometer are auto-zero function to ensure precision torque measurement, select all functions from user-friendly keypad, time stop feature to measure viscosity at precise user specified time interval, time to torque feature to measure the time interval for sample to reach user defined torque value, senses and displays continuously viscosity (cP or mPa·s), temperature (°C or °F), % torque, speed (rpm) and spindle used.
| Tragacanth (g) | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.5 |
| Viscosity (cP) ( x ± SD) | 2.72 ± 0.98 | 2.45±0.48 | 2.92± 0.88 | 2.98 ± 0.46 |
- Plot a graph of height of sedimentation formed after centrifuge against the composition of tragacanth(g). Give your explanations.
| Tragacanth (g) | Before centrifuge (mm) | After centrifuge(mm) | Height ratio |
| 0.0 | 240 | 60 | 4.00 |
| 0.1 | 50 | 140 | 0.35 |
| 0.3 | 79 | 14 | 5.64 |
| 0.5 | 20 | 180 | 0.11 |
For this experiment, centrifuges Is used to investigate the effect of different amount of tragacanth on the height separation produced from the suspension after undergoes centrifugation at 1000 rotation per minute for 5 minutes within 25ºC. Based on centrifugation theory, centrifuge helps to separate suspended material from the mediums they are mixed with. Particles of higher density or larger size typically travel at a faster rate and at some point will be separated from particles less dense or smaller. This can be explained by Stokes equation. Sedimentation rate will decrease as the medium viscosity increases, whereas increases as the gravitational force. Theoretically, theory, the result would be decreased in the ratio separation as the amount of tragacanth used increase. This is because tragacanth acts as a suspending agent, in which it imparts viscosity to the solution, besides forming film around particles and decrease interparticle attraction. It also acts as thickening agent which is important in the increase of viscosity of the solution that helps in preventing sedimentation of the suspended particles. Therefore, there might be some errors during preparation that lead to increasing in height ratio which conducted by group 3
- What is the function of each material that is used in the suspension formulation? How is the use of different amount of Tragacanth affect the physical characteristic and stability of a suspension formulation?
Chalk is an adsorbent and antacid and is an ingredient of mixture and powders used in the treatment of diarrhea. Tragacanth forms viscous solutions or gels with water, depending on the concentration. It is used as a suspending agent. Concentrated peppermint water is a carminative. It has mildly antiseptic properties. Double strength chloroform water acts as carminative, flavouring agent and preservative. Syrup BP is a sweetening and flavoring agent. Varied amount of Tragacanth will affect the physical characteristic of the suspension either it will be rough or smooth. The stability of suspension which use Tragacanth is good and but on prolonged storage is hard to redisperse. Suspensions that do not use Tragacanth do not have good stability and the solid particles inside will sediment rapidly but easy to redisperse.
CONCLUSION
We can evaluate the effect when using varied amount of Tragacanth and this will influence the physical characteristics and stability of the suspension.
REFERENCES
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Viscometer#Rotational_viscometers
- http://www.brookfieldengineering.com/products/viscometers/laboratory-dv-i.asp